2025 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ Report for Desktop as a Service
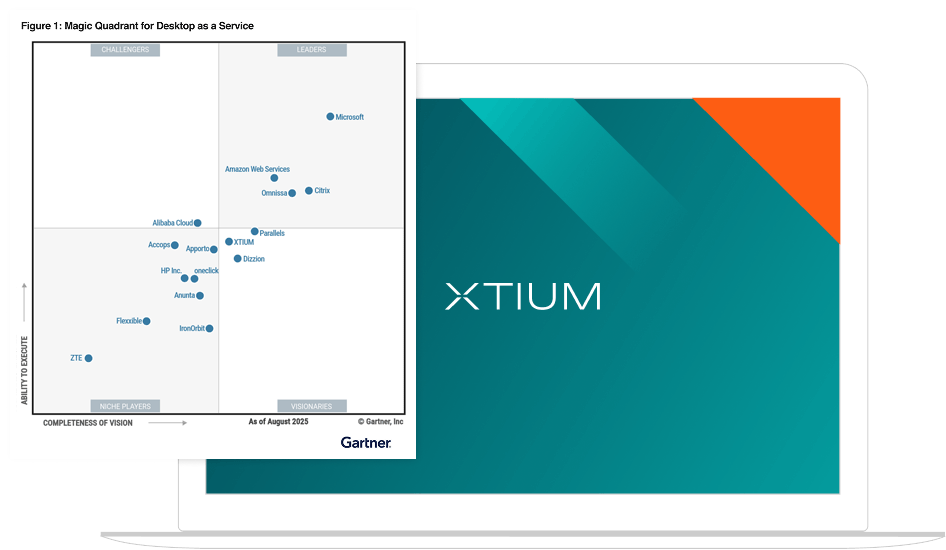
Market Overview
Gartner rarely speaks to an organization that is planning to deploy a new on-premises VDI solution. Net-new deployments are almost exclusively using DaaS, and on-premises deployments are either migrating to DaaS or moving to a cloud control plane, except for a few land-locked use cases. Gartner forecasts that DaaS spending will grow from $4.3 billion in 2025 to $6.0 billion in 2029, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.9%. 1 The DaaS market continues to benefit from on-premises VDI market challenges, including the costs of hypervisor licenses increasing for some customers.
Total cost of ownership for DaaS, especially when users couple it with thin-client endpoints, is now lower than that of a laptop PC for many use cases. Enterprises continue to increase the mix of DaaS within their estates, but most are deploying DaaS for specific use cases rather than a complete PC replacement.
The DaaS market has three key distinct types of offerings, with vendors positioning their products in one or more of the three segments:
Self-assembled DaaS
Vendor-assembled DaaS
Vendor-managed DaaS
Traditionally, cost savings when compared with physical PCs was not a driver for DaaS adoption, but this has now changed. With cost as an adoption driver, enterprises focus acutely on DaaS vendors’ cost-optimization capabilities, with most vendors offering more basic scaling and power management, while other vendors use AI technology to avoid over- and underspecifying the virtual desktop configurations.
By 2027, virtual desktops will be cost-effective for 95% of workers compared to 40% in 2019.By 2027, virtual desktops will be used as the primary workspace for 20% of workers, up from 10% in 2019.
Market Definition/Description
Gartner defines desktop as a service (DaaS) as the provision of virtual desktops by public cloud or other service providers. DaaS provides desktop or application end-user experiences from virtual machines (VMs) accessed using a remote display protocol. DaaS vendors incorporate a fully managed control plane service into their offerings, which facilitates user connections and provides a management interface. DaaS can be delivered preconfigured as a service. Alternatively, it can be delivered as a platform, in which case the client is responsible for assembly, configuration and management. DaaS is charged through subscription- or usage-based payment structures.
DaaS solutions allow remote workers, offshore workers, third-party employees, contractors, frontline workers and office workers to access virtual desktops hosted in the cloud. DaaS solutions include technology that enables centralized management of VMs. DaaS virtual desktops can be configured for a variety of use cases associated with contact center workers, process workers, information workers and workers who require high-performance computing or rich graphics.
Mandatory Features
Common Features
Mandatory Features
Mandatory features in this market include:
- A cloud control plane hosted by a public cloud or other service provider. DaaS operations are performed from this control plane, which also brokers connections to VMs. The control plane is managed and maintained by the vendor.
- A remote desktop protocol that provides secure access to virtual desktops or applications.
- Support for the ability to connect from a range of endpoints, including those running Windows, macOS and less common browsers.
- A tool to manage virtual desktop resources, users and assignments.
Common Features
Common features in this market include:
- The ability to orchestrate persistent and nonpersistent compute and storage resources for Windows 10/11 desktop experiences or for similar experiences on a Windows Server OS running single-session or multisession VMs.
- Management technology to allow central updating or management of VM images.
- Vendor-provided compute and storage resources.
- Application-hosting capabilities (published app). Real-time audio and video optimization for unified communications solutions, including Microsoft Teams, Cisco Webex, Zoom and solutions that support WebRTC.
- Monitoring of virtual desktop and application usage, as well as user experience, and performance.
- User profile management.
- Application layering and masking.
- Support for graphics processing unit (GPU) workloads.
- Integration or extension of the client’s network into the DaaS environment.
- Multicloud and hybrid deployment options. IT service management (ITSM) tool and configuration management database (CMDB) integration.
- Digital employee experience (DEX) or digital experience monitoring (DEM) tool integration.
- Support for access from nontraditional endpoint operating systems, including Linux, iOS, Android, Chrome OS, IGEL OS, eLux OS, Dell ThinOS and Stratodesk NoTouch OS.
Vendor Strengths and Cautions
Accops
Accops is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Accops DaaS provides self-assembled, vendor-assembled and vendor-managed options. It provides the technology for JioPC, a consumer and enterprise DaaS available in India. Accops’ offerings can leverage its own proprietary virtual desktop technology or integrate with Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop. Accops delivers a range of virtual desktops, including Windows and Linux, in configurations that support CPU and GPU configurations.
Accops’ installed base resides in Asia (90%), North America (5%) and Europe (5%). Client sizes range from 0-99 employees (39%), 100-4,999 employees (80%) and over 5,000 employees (10%). Top verticals are consulting/business services, financial services and technology/telecom.
Strengths
- Operations: Accops operates virtual desktops globally from its operations center in India. Accops has invested in automating its operations and its JioPC offering, which will benefit smaller customers by enabling zero-touch, low-skill deployment and management.
- Overall viability: Accops is owned by Reliance Jio Infocomm, which is itself part of the largest commercial conglomerate in India, with over 300,000 employees providing financial and operational stability. Reliance Jio hosts the Microsoft Azure cloud platform in data centers across India as part of a 10-year partnership agreement signed in 2019.
- Sales execution/pricing: Accops offers both perpetual and subscription licenses, with options for named, concurrent and device-based licenses. This flexibility also extends to deployment options, where customers can select a range of options — from self-assembled, where Accops solely provides the control plane, to fully managed DaaS.
Cautions
- Global support strategy: Accops’ global support strategy primarily relies on operations located in India. A direct regional presence is maintained in the Middle East and Japan. On-site presence and support in other global regions typically depend on channel partners or system integrator (SI) partners. Accops provides customer support in English, Hindi and Japanese. Clients outside of these three regions could experience delays when resolving issues.
- Compliance gaps: Accops holds ISO 27001 certification but no other compliance certificates. Prospects and clients must clarify when compliance certificates they require will be obtained.
- Marketing strategy: Accops’ brand awareness outside India, the Middle East, Africa and Japan remains low, even though it has raised its marketing budget, added new marketing channels, and increased its presence at events and online. As a result, customers outside of India, the Middle East, Africa and Japan might overlook Accops’ offerings in their DaaS procurement evaluations.
Alibaba Cloud
Alibaba Cloud is a Challenger in this Magic Quadrant. Its DaaS offering, Elastic Desktop Service, is a vendor-assembled DaaS built on proprietary technologies, including the Adaptive Streaming Protocol for remote desktop delivery, hyperscale cloud, custom-built control plane and dedicated endpoints. It offers Windows and Linux virtual desktops with CPU- or GPU-enabled VMs. Other features include autoscaling, dynamic configurations, and no fees for hibernated or powered-down desktops.
Gartner estimates that Alibaba Cloud’s installed base is primarily within China (over 50%), then Asia (over 25%), and then the rest of the world. Alibaba targets customers with less than 5,000 employees. Gartner estimates this to be more than 80% of Alibaba’s customers, with less than 20% having over 5,000 employees. Top verticals are financial services, education and manufacturing.
Strengths
- Operations: Alibaba has a global operations center located in Singapore and regional service centers in Malaysia, Mexico and Portugal. Alibaba Cloud has a wide range of regional compliance certifications, including HIPAA, PCI-DSS, SOC 3 and more, and the solution is designed to enable data residency.
- Overall viability: Alibaba Cloud’s position as part of the $320-billion publicly traded Alibaba Group provides strong financial backing and stability. Its consistent investment in DaaS, operations and sales reflects a long-term commitment to growth and innovation.
- Product of service: Alibaba’s cloud offering is based on its own IP, allowing it full control over the entire technology stack and operations. Alibaba delivers more Linuxbased virtual desktops than most other vendors, primarily leveraged by clients for developer use cases.
Cautions
- Vertical/industry strategy: Alibaba Cloud’s “vertical scenario optimization” requires self-configuration to meet industry-specific requirements and compliance. This may present additional complexity or risk for organizations with strict regulatory or specialized needs.
- Marketing execution: Alibaba has had limited success at expanding customer awareness of its offering in North America and Europe, which are the largest DaaS markets globally. Despite increasing its marketing budget and active channels, Alibaba Cloud’s messaging has resulted in growth primarily within China and the Asia region.
- Ecosystem and integration strategy: Elastic Desktop Service lacks capabilities that other DaaS providers offer and customers expect, such as deeper, applicationspecific optimizations for Microsoft Teams and other unified communications. This indicates a gap in its integration strategy for widely used enterprise tools outside of China.
Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a Leader in this Magic Quadrant. Amazon WorkSpaces offers vendor-assembled DaaS, self-assembled DaaS and web applications. AppStream offers application virtualization with multisession configurations. AWS delivers a range of virtual desktops, including Windows and Linux, with CPU- and GPU-enabled VMs.
Gartner estimates 45% of AWS’s DaaS clients are located in North America, 30% in Europe and 25% in the rest of the world. Gartner estimates that 5% of DaaS clients have 0-99 employees, 40% have 100-4,999 employees and 50% have over 5,000 employees. The top verticals are technology and telecom, financial services and manufacturing.
Strengths
- Operations: AWS provides out-of-the-box monitoring and alerting for WorkSpaces deployments, integration with AWS platform for automation, and integration with ControlUp for digital employee experience (DEX) tool capabilities. Amazon Q, a chatbased interface, assists with basic use cases for troubleshooting, developing scripts and managing resources.
- Geographic strategy: AWS delivers DaaS services in 17 regions for persistent workloads and 15 regions for pooled workloads, covering North America, South America, Europe, Asia/Pacific, the Middle East and Africa. With the AWS Enterprise Support plan, technical account managers provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Portuguese, Spanish and Thai.
- Vertical/industry strategy: AWS has the scale to address the needs of multiple industry verticals and large global multinational conglomerates. Amazon WorkSpaces offers vertically aligned capabilities and robust compliance frameworks. These capabilities extend to identity verification, such as smart card authentication and high-performance computing.
Cautions
- Marketing execution: AWS uses multiple marketing channels and has started to use influencers to expand its reach beyond traditional channels. This strategy, while sound, has so far failed to see significant displacement of competitors. Longer term, the lack of displacement could impact its ability to innovate at the same rate as other Leaders.
- Feature development: The pace of feature development remains slower than that of other Leaders in this Magic Quadrant. AWS lags in some key innovation areas, lacking the personalization that employees expect when using nonpersistent desktops. Clients will need to engage with AWS to understand if and when any feature gaps will be filled.
- Technical expertise requirements: While Amazon WorkSpaces offers broad applicability and aims for simplified deployment, Gartner clients report they need specific technical expertise for specialized or complex use cases. Examples of this expertise include peripheral support, developer desktops and custom configurations.
Anunta
Anunta is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Anunta offers vendor-assembled and vendor-managed DaaS options. Anunta’s proprietary technology, EuVantage, enables automation, orchestration and low-touch DaaS operations. Anunta delivers a range of virtual desktops, including Windows and Linux, with CPU- and GPU-enabled virtual machines. The vendor leverages third-party remote desktop protocols, third-party brokers, hyperscale clouds and its own private cloud.
Anunta’s installed base resides in Asia (67%), North America (23%) and the Middle East (10%). Client sizes range from 0-99 employees (2%), 100-4,999 employees (10%) and over 5,000 employees (88%). Top verticals are financial services, consulting and business services, and technology and telecom.
Strengths
- Product or service: Anunta offers a breadth of remote desktop network protocols that meets a broad range of use cases aligned to enterprise scale deployments. Anunta leverages DaaS offerings from Citrix, Omnissa, Microsoft and AWS, enhancing these services with its own operations tool, automations, orchestration and cost optimization.
- Offering (product) strategy: Anunta offers services for the full life cycle of a DaaS offering while remaining platform independent. This allows enterprises to mix virtual desktop technologies and clouds to align to specific requirements. Real-time dashboards leverage machine learning to accurately highlight and respond to anomalies. Anunta’s DaaS services strategy is to maximize performance and optimize costs using a predictive service model.
- Market responsiveness/record: Anunta’s offering is widely available and can be purchased by enterprises. Some virtualization vendors white-label their owned, vendor-managed DaaS offerings using Anunta. The service is also leveraged by global system integrators. Anunta has expanded its global footprint based on demand and has consistently released technology enhancements ahead of mainstream adoption, including recent AI functionality.
Cautions
- Marketing execution: Market awareness of Anunta’s brand and offering is limited, and prospects may find it difficult to navigate the breadth of services provided.
- Localized support gaps: While Anunta’s offering is available globally, clients may encounter limitations in receiving comprehensive local-language support or nativespeaker assistance across all geographical regions. Anunta primarily offers support in English, Hindi and Japanese, which could lead to communication challenges or delayed resolution for issues requiring deep regional understanding.
- Sales execution/pricing: Anunta’s sales strategy relies on third-party system integrators, driving premium pricing. Pricing is mostly an overlay price on top of the DaaS hosting fees and any DaaS license fees.
Apporto
Apporto is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Its Desktop as a Service, Digital Workspaces and Virtual Computer Labs offerings provide vendor-managed DaaS. Apporto uses its own proprietary technology, including its HyperStream protocol, cloud control plane, and Portia AI language model and virtual assistant. It leverages hyperscale cloud vendors for hosting. Apporto delivers a range of virtual desktops, including Windows and Linux, with CPU- and GPU-enabled VMs.
Apporto’s installed base resides in mainland North America (89%), Europe (8%) and the rest of the world (3%). Client sizes range from 0-99 employees (7%), 100-4,999 employees (54%) and over 5,000 employees (39%). Top verticals are education, financial services and manufacturing.
Strengths
- Business model: Apporto’s performance-based SKUs with concurrent-user pricing provides customers with more predictability than consumption-based models. Apporto offers volume flexibility through the contract term but limits it to three changes per year.
- Vertical/industry strategy: Apporto offers specific integrations for education, including learning management systems, virtual classrooms, virtual labs and cybersecurity labs. Gartner estimates that almost 70% of Apporto use is for education.
- Sales execution/pricing: Apporto has a defined pricing model where purchase volume primarily drives tiered discounts. Its sales execution is primarily direct, with channel and specialist partnerships (e.g., learning management system vendors). Much of Apporto’s direct sales growth is driven by word of mouth.
Cautions
- Marketing execution: Despite multichannel marketing, the awareness of Apporto among target clients remains low. Clients should validate long-term roadmaps with Apporto, as limited market share could impact its long-term ability to invest in its platform.
- Operations: Apporto employs a low number of operations and engineering staff compared with other vendors in this Magic Quadrant. This may cause support response challenges as it scales into new regions.
- Geographic deployments: Apporto has expanded from selling in North America to other regions, including Europe. Ninety-seven percent of its users are in North America or Europe. Prospects outside of North America and Europe will need to determine if Apporto is fully capable of supporting their DaaS needs.
Citrix
Citrix Citrix is a Leader in this Magic Quadrant. Citrix DaaS is most often leveraged for selfassembled DaaS use cases, but Citrix also offers vendor-assembled DaaS. There will be a higher return on investment for clients that utilize more components of the Citrix bundles. In addition to DaaS, these components include application delivery controllers, a hypervisor, device management and a thin-client operating system.
Citrix’s installed base resides in North America (56%), Europe (33%) and the rest of the world (11%). Gartner estimates client sizes range from 0-5,000 employees (15%) and over 5,000 employees (85%). Gartner estimates that the largest industry verticals for Citrix are financial services, healthcare and the public sector.
Strengths
- Product or service: Citrix has a comprehensive enterprise-class offering that can be configured to meet the most complex requirements. Citrix’s DaaS offering is an ideal solution for large multinational clients with regulatory requirements. Its intellectual property, especially its protocol and management plane, alongside its integrations, allows more use cases to be addressed than with other vendors.
- Market responsiveness/record: Citrix is the longest-standing desktop virtualization vendor, known for its responsiveness to market needs. Its agile and customerfocused roadmap prioritizes customer requests alongside work to integrate technology from strategic acquisitions.
- Offering (product) strategy: Citrix’s strategy is to deliver an experience “as good or better than a local PC.” It is achieving this through advancements in its network protocol and cost management, the latter allowing higher-performance virtual desktops at the same cost. Its AI investments and strategy to release Citrix Copilot enable large clients to reduce their operational complexity.
Cautions
- Sales execution/pricing: Citrix bundles its DaaS offering with other technologies; for example, thin-client operating system management, application delivery controllers and analytics. Clients tell Gartner they find the bundle expensive for DaaS unless they exploit other included technologies.
- Sales experience: Citrix operates a two-tier sales experience. Sales under $250,000 per year are handled primarily through distributors and resellers, with Citrix’s direct sales teams focused on the largest clients. Distributors may offer flexible subscription terms to smaller customers, but larger customers typically face difficulty negotiating contract durations shorter than three years.
- Limited direct managed service offerings: Citrix does not offer extensive managed services beyond its core DaaS control plane, such as image management or OS/application patching. The Citrix model necessitates that clients either maintain in-house expertise or engage third-party providers for these operational aspects, contrasting with offerings containing a broader suite of vendor-managed DaaS capabilities.
Dizzion
Dizzion is a Visionary in this Magic Quadrant. Its DaaS offering, Dizzion DaaS, provides vendor-assembled and vendor-managed solutions (Dizzion Cloud PC was launched after the cutoff for this research). Dizzion’s core technology is the proprietary, cloud-native Frame platform, which it fully owns and develops in-house for orchestration, session brokering, front-end user experience (UX) and remoting protocol.
Dizzion’s installed base resides in North America (50%), Europe (40%) and the rest of the world (10%). Gartner estimates client sizes range from fewer than 5,000 employees (60%) to over 5,000 employees (40%). Top verticals are manufacturing, consulting and business services, and education.
Strengths
- Product or service: Dizzion’s proprietary, cloud-native Frame platform architecture enables true hybrid and multicloud DaaS deployments across a broad range of public clouds. Customers that require multicloud and hybrid deployments will benefit from public cloud support, including AWS, Azure, GCP and IBM Cloud VPC, in addition to Nutanix or VMware vSphere on-premises.
- Offering (product) strategy: Dizzion’s product strategy focuses on digital workspace solutions, allowing for greater agility in development and innovation compared with vendors for which DaaS is a minor portfolio component. Dizzion offers a browserfirst user experience, benefiting unmanaged endpoints — for example, in education and third-party access use cases — alongside app-based access for managed endpoints.
- Business model: Dizzion’s flexible, multicloud DaaS offerings, including consumption-based pricing via Flex Credits, enables customers to align costs with usage and avoid vendor lock-in with public clouds. Dizzion’s focus is clients with 100-4,999 employees, allowing it to deliver capabilities for the requirements of this market segment. Gartner Peer Insights reviews highlight the ease of deployment and level of customer support.
Cautions
- Operations: Dizzion has a lower-than-average number of engineers and operational staff, and it maintains and is actively converging two offerings into a single platform. Clients and prospects should be aware that the combination could impact Dizzion’s responsiveness to feature and support requests.
- Geographic strategy: Dizzion targets all regions except Africa and China (Region). A global sales strategy like this is especially challenging for smaller vendors. Resources may be directed toward the building of its sales pipelines in non-core regions, which may impact the level of innovation clients observe.
- Sales execution/pricing: Dizzion was only mentioned as a top-three competitor by one of the other 15 vendors in this Magic Quadrant. A continued lack of competitiveness may mean clients see slower development of new features due to a lack of organic funding.
Flexxible
Flexxible is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Flexxible includes vendor-assembled and vendor-managed capabilities built on top of Citrix, Omnissa Horizon, Parallels, Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop and Amazon Workspaces. It offers a centralized control plane hosted in the cloud or customer environment. The FlexxDesktop DaaS offering includes automation and monitoring. It can be purchased as part of a bundle with FlexxClient that includes digital employee experience and endpoint operations capabilities.
Gartner estimates that Flexxible’s installed base resides in North America (25%), Europe (60%), Latin America (10%) and the Middle East (5%). Client sizes range from 0-99 employees (0%), 100-4,999 employees (35%) and over 5,000 employees (65%). Top verticals are government, energy and financial services.
Strengths
- Market responsiveness: Flexxible primarily targets enterprise clients, managed service providers and system integrators, but it has also started to position itself as a cost-effective European provider. This strategy makes Flexxible more attractive to European clients seeking geo-repatriation or global clients seeking cost-optimized DaaS solutions.
- Overall viability: Flexxible, founded in 2008, launched its Enterprise VDI offering in 2012, upgrading this to FlexxDesktop DaaS in 2021. Flexxible has a portfolio of offerings for automating endpoint operations and DEX, which are integrated to provide end-to-end capabilities for clients.
- Product or service: Flexxible offers strong vendor-managed solutions utilizing other leading DaaS vendors’ solutions. It is able to gather requirements and tailor an optimal solution built for MSPs and large enterprises. Flexxible also utilizes experience-level agreements (XLAs) to enhance services and proactive operations.
Cautions
- Customer experience: Flexxible continues to have a small customer base and is rarely mentioned by Gartner clients during inquiries. Prospective clients should work with Flexxible to ensure design and deployment projects are short in duration. Custom architectures may be a challenge or not supported.
- Marketing execution: Flexxible has focused its marketing on very few geographies and customer sizes. This leads to low customer awareness and low levels of adoption of Flexxible’s DaaS offering, resulting in less ability to keep pace with client requirements.
- Innovation: Flexxible has offered capabilities for automation and DEX for some time but has not introduced many product enhancements during the last two years. Clients should ensure existing functionality meets current and expected requirements.
HP Inc.
HP Inc. is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Its HP Anyware offering is a selfassembled DaaS solution. HP Anyware includes the control plane service, protocol, agents and client applications in the total bill. Cloud infrastructure can either be purchased directly through the cloud vendor or through HP’s cloud reseller program. The control plane, agents and remote protocol are all HP intellectual property. HP offers a wide range of VM operating system options, including Windows, Linux, and macOS. HP Anyware also integrates with Windows 365.
HP Inc.’s installed base resides in North America (50%), Europe (30%), Asia (14%) and the rest of the world (6%). Client sizes range from 0-99 employees (5%), 100-4,999 employees (35%) and over 5,000 employees (60%). Top verticals are entertainment, technology and telecom, and manufacturing.
Strengths
- Overall viability: HP Inc. is unique due to its full range of enterprise hardware, including PC devices, thin clients, room-based unified communications hardware, printers, and peripherals such as keyboards, mice and headsets. HP also provides software to help manage endpoints and its HP Workforce Experience Platform DEX tool. HP provides a one-stop shop for physical and virtual desktop requirements and is actively focused on enhancing the digital workplace through its “Future of Work” strategy.
- Operations: The HP Anyware architecture offers robust business continuity and high-availability configurations, including automatic regional failover that utilizes multilocation host pools or Windows 365. Its support is globally available, and its clients benefit from both host and remote desktop protocol monitoring, resulting in better employee experiences.
- Vertical/industry strategy: HP Inc. targets enterprise use cases requiring highsecurity or high-fidelity experiences. HP’s scale means it can allocate staff skilled in industry verticals alongside DaaS specialists during the sales, design and deployment phases.
Cautions
- Marketing execution: HP Inc. is relatively new to the DaaS market, entering through its acquisition of Teradici in 2021 and the subsequent development of HP Anyware. HP adoption to date has generally been for specialist and high-performance use cases or for its PCoIP protocol. Clients will need to engage with HP to fully understand and apply its capabilities.
- Lack of experience-level agreements: HP Anyware does not include XLAs. This contrasts with a growing industry trend toward measuring and guaranteeing user experience through XLAs.
- Marketing strategy: HP Inc. is not mentioned by any other vendor in this Magic Quadrant as a top-three competitor encountered on shortlists, which emphasises its need to increase HP Anyware market awareness in line with awareness of its PCoIP protocol. HP has run in-person events, and digital and account-based marketing globally with targeting for key verticals. Low market awareness can lead to lower adoption levels and in turn, less innovation, which is visible to clients.
IronOrbit
IronOrbit is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Its vendor-managed DaaS solution, INFINITY Workspaces, is hosted in its own private cloud environment and on Microsoft Azure. IronOrbit also utilizes Omnissa Horizon for GPU-based virtual desktops and application delivery. IronOrbit has deeper skills than most DaaS vendors for use cases that require rich graphics and GPUs.
Gartner estimates more than 90% of IronOrbit’s installed base resides in North America, with less than 10% in the rest of the world. Estimates for IronOrbit’s client sizes are 0-99 employees (less than 5%), 100-2,999 employees (15%) and more than 3,000 employees (over 80%). Key verticals are manufacturing, transportation and logistics, and consulting and business services.
Strengths
- Business model: IronOrbit offers a customizable and scalable vendor-managed product with strong customer service and comprehensive SLAs. IronOrbit can tailor its offering to specific technical and operational needs with little effort or skills required by customers.
- Offering (product) strategy: IronOrbit uses customer service managers with defined KPIs, which generally results in long-term client relationships. It also has a roadmap focused on global expansion and integration of AI for monitoring and automation, which reduces client effort and increases immediacy of client service requests.
- Vertical/industry strategy: IronOrbit primarily focuses on industry verticals utilizing GPU-enabled applications, including manufacturing, transportation and logistics, and engineering. It succeeds in providing powerful graphics processing for demanding applications and has optimized 3D design and rendering software from Dassault Systèmes and AutoCAD.
Cautions
- Marketing execution: IronOrbit’s focus on GPUs has resulted in limited broader market awareness and lower mind share. This niche positioning may impact the pace of broader product investment. Clients should ensure IronOrbit’s roadmap aligns with their needs.
- Customer experience: IronOrbit only provides its highest customer service offerings through its premium support package. Clients that do not procure premium support will be entitled to the default essential support, which delivers an experience consistent with lower levels of support.
- Geographic strategy: IronOrbit users and workloads can reside in multiple regions. However, IronOrbit continues to focus on North America. Clients outside of North America should assess regional requirements when engaging with IronOrbit.
Microsoft
Microsoft is a Leader in this Magic Quadrant. Its DaaS offerings include Azure Virtual Desktop, Windows 365 and Microsoft Dev Box. These offerings provide self-assembled and vendor-assembled DaaS. Azure Virtual Desktop, which is consumption-based, includes autoscaling and cost management capabilities. Windows 365 is now positioned for frontline workstyles alongside the initial information worker focus. Microsoft has launched Windows 365 Link, an endpoint device specific to Windows 365.
Gartner estimates Microsoft’s installed base resides in North America (60%), Europe (30%) and the rest of the world (10%). Estimates for Microsoft DaaS client sizes range from 0-99 employees (10%), 100-4,999 employees (60%) and over 5,000 employees (30%). Gartner estimates Microsoft’s top verticals are financial services, the public sector, and consulting and business services.
Strengths
- Platform strategy: Clients with investments in Microsoft 365 may benefit from its DaaS offerings by reducing the number of tools deployed and increasing Azure utilization agreement benefits. No other vendor has such broad capabilities across digital workplace technologies, hyperscale cloud and AI.
- Operations: Microsoft has a robust global infrastructure and has increased its number of hosting regions and the number of regions where it supports data residency over the last year. The scale of its operation is the largest in this Magic Quadrant, making it an ideal offering for clients in all regions and of all sizes.
- Market share: Microsoft delivers a broad range of marketing activity both directly and through its large partner ecosystem. It has mind share and market share, resulting in significant levels of investment in its DaaS offerings, which, in turn, benefits clients and prospects.
Cautions
- Azure Virtual Desktop complexity: Clients using Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop must configure this offering, which is perceived as complex compared to vendormanaged DaaS offerings like Windows 365. Clients often deploy third-party tools to assist in Azure Virtual Desktop operations (e.g., Login VSI, Nerdio). Clients should weigh the cost benefits of Azure Virtual Desktop versus the comparative operational simplicity of Windows 365.
- Cloud PC configuration drift: Microsoft Windows 365 is managed like a physical PC using Microsoft Intune. Clients should be aware that, unlike some VDI configurations that have limited configuration drift and instant deployment of updates, Microsoft Intune takes longer to deploy and there is more configuration drift.
- Product selection: In Gartner’s opinion, Microsoft is prioritizing Windows 365 over Azure Virtual Desktop. Each release of Windows 365 has expanded its use cases (e.g., desktop pools in Windows 365 Frontline shared mode and announced updates to include application hosting). Some use cases can now be addressed by both products. Clients should review their use cases thoroughly before selecting Windows 365 or Azure Virtual Desktop or both.
Omnissa
Omnissa is a Leader in this Magic Quadrant. Omnissa offers self-assembled, vendorassembled and vendor-managed options. The Horizon Control Plane is cloud-hosted and supports on-premises, hybrid and multicloud deployments. The Horizon Cloud integrates with most cloud providers, including Microsoft Azure and AWS. Horizon Blast Extreme is a proprietary protocol and works well with high latency and slow connections; it also supports high-resolution workloads.
Gartner estimates that Omnissa’s installed base resides in North America (55%), Europe (30%) and the rest of the world (15%). Gartner estimates that client sizes range from 0-99 employees (3%), 100-4,999 employees (40%) and over 5,000 employees (57%). Omnissa does not provide metrics regarding customer demographics.
Strengths
- Product or service: Horizon is a strong offering for deployments of all scales. It is a particularly strong offering for clients with hybrid, on-premises and multicloud needs. Horizon Blast Extreme is ideal for clients that require a reliable protocol. Horizon forms part of Omnissa’s end-user services portfolio that also includes endpoint management and DEX tools, which benefits clients seeking a single vendor for physical and virtual desktop solutions.
- Market understanding: Omnissa demonstrates a recognition of customer needs with its broad features that include persistent, pooled and multisession virtual desktops and virtualized applications. For multinational clients and those with multiple use cases, Horizon also provides wide geographic and multicloud support.
- Sales strategy: Omnissa leverages partnerships with the most widely-deployed hyperscale vendors, Microsoft and Amazon. For clients that require hybrid deployments, Omnissa has a unique agreement with Broadcom to sell Horizon and VMware vSphere Foundation for VDI (VVF for VDI) combined offerings.
Cautions
- Lack of XLAs: Omnissa does not offer an experience-level agreement for the Horizon Cloud Service. This contrasts with a growing industry trend toward measuring and guaranteeing user experience through XLAs.
- Overall viability: Omnissa is limited to two main product offerings in a highly competitive market (Horizon and Workspace ONE). Horizon also faces mixed market sentiment due to its past association with Broadcom. Clients should consider these risks for any long-term strategies.
- Customer experience: As a new company, Omnissa faces concerns, expressed during Gartner client inquiries, about its ability to continue providing solid global support. Clients should discuss concerns with Omnissa and prepare mitigation strategies.
oneclick
oneclick is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Its oneclick DaaS Platform is offered as self-assembled, vendor-assembled and vendor-managed, and is mostly utilized by cloud service providers (CSPs). oneclick supports many clouds and is available in hybrid and multicloud configurations. It offers features such as single-session, multisession, published applications, rich graphics, and Windows and Linux virtual desktops.
oneclick’s installed base resides in North America (10%), Europe (70%), Asia (10%), Africa (6%), the China region (2%), and the Middle East and Latin America (under 1% each). Client sizes range from 0-99 employees (22%), 100-4,999 employees (53%) and over 5,000 employees (25%). Top verticals are technology and telecom, retail, and consulting and business services.
Strengths
- Geographic strategy: The large majority of oneclick’s customers are in Europe, and it has continued to focus on growing its presence in North America, China (Region) and Asia. oneclick has a higher proportion of clients in Africa than any other vendor. oneclick highlights its data sovereignty in Europe.
- Business model: oneclick offers tiered service availability up to 99.99% and negotiated SLAs for CSPs. Its turnkey platform integrates automation, making it an ideal offering for clients that lack expert staff in this area. oneclick also offers a simplified licensing model as well as individual product licensing options.
- Product or service: oneclick has extensive cloud platform support with hybrid and multicloud offerings. oneclick can provide automation and digital experience monitoring for simplified management and better user experience.
Cautions
- Marketing execution: oneclick’s marketing is mostly focused on online channels, videos and webinars. Despite multiple marketing channels, clients rarely mention oneclick during inquiry calls. Clients should validate long-term roadmaps with oneclick, as limited market share could impact its long-term ability to invest in its platform.
- Customer experience: oneclick has broad service and platform offerings, but its primary customers are CSPs that have lots of clients with 0-4,999 employees. Clients with more than 5000 employees buying direct from oneclick should ensure its operations and support meets requirements.
- Innovation: oneclick focuses on core DaaS capabilities. Clients with greater technical capabilities should verify oneclick can meet their specific requirements.
Parallels
Parallels is a Visionary in this Magic Quadrant. Its Parallels DaaS offering is hosted on Microsoft Azure and is available as self-assembled and vendor-assembled. Parallels’ features include multisession, single-session, dedicated, pooled nonpersistent, published app, vGPU, and full Windows or Linux desktops. Parallels has an on-premises offering, Parallels RAS, which can support hybrid, cloud and multicloud implementations with a single licensing model based on concurrent users. For cloud deployments, Parallels DaaS uses a single licensing model based on named users.
Parallels’ installed base resides in North America (41%), Europe (45%) and the rest of the world (14%). Client sizes range from 0-99 employees (50%), 100-4,999 employees (38%) and over 5,000 employees (12%). Top verticals are consulting and business services, healthcare and manufacturing.
Strengths
- Offering (product) strategy: Parallels has a strong offering for cloud, hybrid and onpremises architectures. It provides a wide range of features while focusing on simplified administration. This combination synergizes a capable solution for most small and midsize organizations.
- Overall viability: Parallels continues to gain customers and grow in features, including a new cloud-native control plane for Parallels DaaS. Its offerings meet most customers’ needs and have clear licensing, and clients cite ease of use.
- Sales strategy: Parallels is taking advantage of low client sentiment toward some of the larger DaaS and VDI vendors to sell itself as a solid offering with simple licensing and administration. Given the complexity of transitioning between vendors, this effective strategy is working to drive customers to evaluate its offerings. Parallel’s approach leverages a partner ecosystem that includes value-added resellers, managed service providers and system integrators.
Cautions
- Vertical/industry strategy: Parallels lacks broad vertical coverage and is limited in security and compliance certifications. Clients should evaluate Parallels’ offerings against any specific industry and compliance requirements.
- Professional and managed services: Parallels’ does not offer dedicated professional or managed services using in-house resources. Clients and prospects should validate who will support deployment projects and map a clear list of responsibilities between themselves, Parallels and the services partner.
- Market responsiveness/record: Parallels’ pace of cutting-edge innovation lags behind competitors. For example, AI capabilities are limited to analyzing and improving login times only in the Parallels RAS and not in the Parallels DaaS offering. Clients should verify current offerings meet their specific requirements.
XTIUM
XTIUM is a Visionary in this Magic Quadrant. Its XTIUM DaaS offering provides vendorassembled and vendor-managed DaaS, including desktop and application virtualization options. XTIUM’s DaaS offering is available globally with support centers located in North America, Europe and Asia. This vendor complements technology from Citrix, Microsoft Azure and Omnissa with its own intellectual property for DaaS operations and delivers a range of virtual desktops running Windows with CPU and GPU options.
XTIUM’s installed base resides in North America (90%), Europe (6%) and the rest of the world (4%). Gartner estimates that 5% of clients have 0-99 employees, 60% have 100- 4,999 employees and 35% have over 5,000 employees. The top verticals are travel and hospitality, healthcare and pharmaceuticals, and financial services.
XTIUM was formed through the business combination of ATSG and Evolve IP. ATSG was featured in the 2024 Magic Quadrant.
Strengths
- Product or service: XTIUM has increased its product breadth to include Citrix and Omnissa as its primary brokers. Its services provide complex DaaS configurations without requiring clients to have deep technical skills. XTIUM offers complementary network, enterprise service desk, cloud, security, and unified communications managed services.
- Offering (product) strategy: XTIUM’s solution is built on its hosted cloud management plane, XTIUM Cloud Manager. It has embedded DEX and AI capabilities to enhance performance, provide proactive operations and increase levels of automation.
- Sales strategy: XTIUM’s sales strategy combines direct engagement with a strong channel partner program. XTIUM emphasizes the value of its DaaS solution through clear pricing and targeted messaging, resulting in clients generally becoming longterm customers.
Cautions
- Market visibility: XTIUM leverages a wide range of marketing channels but has grown its installed base less than other vendors in this market. Prospects should be aware that low growth levels due to lack of market awareness may impact DaaS offering development budgets.
- Vertical/industry strategy: XTIUM is actively used across a broad range of industry verticals but does not provide any vertical SKUs. XTIUM has certifications like HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOC 2 and ISO 27001; however, prospects should be aware that some deployments will typically require additional customization for highly specialized regulatory needs.
- Business model: While XTIUM emphasizes its commitment to digital employee experience, it does not have any credit/compensation structure related to user experience metrics if those are not met. Clients prioritizing contractually guaranteed user experience outcomes with associated financial remedies should factor this absence into their negotiations.
Workspot
ZTE is a Niche Player in this Magic Quadrant. Its offering is most commonly referred to as ZTE Cloud PC. Cloud PC is a vendor-managed offering that is designed and deployed perclient and managed from ZTE’s cloud control plane. ZTE offers virtual desktops that run on Windows and Linux. ZTE states it supports all major unified communications offerings, but Microsoft Teams, Cisco Webex and Zoom do not list ZTE as having such integrations. ZTE sells directly to enterprises and also through telecom vendors. Its offering is developed in-house, including its Remote Access Protocol (RAP), ICE protocol and endpoint devices.
ZTE’s installed base resides in the China region (98%) and Asia (Thailand [2%]). Gartner does not consider ZTE Cloud PC viable for enterprises outside China (Region) and Thailand, as it does not operate or sell outside these markets. Client sizes range from 0-99 employees (90%), 100-4,999 employees (6%), and over 5,000 employees (4%). Its largest deployment is 50,000 users. ZTE’s top vertical is technology and telecom, and it primarily sells to CSPs.
Strengths
- Product or service: For enterprises located in China (Region), especially those in technology and telecom, ZTE offers a functional virtual desktop and virtual desktop endpoint offering. ZTE has significant experience with GPU workloads.
- Operations: ZTE has 10 regional development and operations centers for clients in China (Region) and Thailand. Within its core regions, it has more than 10 delivery centers.
- Vertical/industry strategy: ZTE has specific IP related to manufacturing, with offerings that integrate the Cloud PC with edge devices and 5G systems. ZTE has also developed multimedia classrooms, making Cloud PC particularly strong for clients and prospects in education.
Cautions
- Geographic strategy: ZTE’s focus within China (Region) and Thailand limits its geographic potential. Clients outside of China (Region) and Thailand will need to consider alternative vendors.
- Marketing execution and strategy: ZTE’s offering is not well-known outside of the China region. Within the region, its offering is often white-labeled by CSPs, which restricts awareness of its brand. Enterprise clients should ensure ZTE prioritizes their requirements and is not solely focused on its CSP clients.
- Product strategy: ZTE targets small businesses and consumer use cases. Prospects with more than 100 employees may not have their DaaS needs satisfied and should evaluate other vendors in this market.
Vendors Added & Dropped
We review and adjust our inclusion criteria for Magic Quadrants as markets change. As a result of these adjustments, the mix of vendors in any Magic Quadrant may change over time. A vendor's appearance in a Magic Quadrant one year and not the next does not necessarily indicate that we have changed our opinion of that vendor. It may be a reflection of a change in the market and, therefore, changed evaluation criteria, or of a change of focus by that vendor.
Added
Accops: Accops DaaS now meets the inclusion criteria.
HP Inc.: HP Anyware now meets the inclusion criteria.
XTIUM: ATSG merged with Evolve IP and rebranded the new company as XTIUM on 18 March 2025.
ZTE: ZTE now meets the inclusion criteria.
Dropped
ATSG: ATSG merged with Evolve IP and rebranded the new company as XTIUM on 18 March 2025.
Workspot: Workspot no longer meets the inclusion criteria. It has not ranked among the top 20 in the Customer Interest Indicator (CII) defined by Gartner for the DaaS Magic Quadrant. The analysts thoroughly reviewed the results of the CII and confirmed that it aligns with client demand indicators we are seeing in this market.
Inclusion & Exclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria have changed from 2024, when vendors could qualify with 100,000 CPU-enabled virtual desktops. This number increased to 150,000 for 2025. In 2024 the inclusion criteria required 25,000 virtual machines under management, which increased to 30,000 in 2025. Gartner expects these criteria to rise in future years.
To qualify, vendors met the following criteria:
Market participation: Must sell desktop as a service aligning to the market definition.
Market traction: DaaS offering must meet the following criteria:
- Vendor has been active in the virtual desktop infrastructure, server-based computing or desktop as a service market(s) before 1 April 2025
- DaaS offering(s) assessed have been generally available on or
- before 1 April 2025
- 150,000 monthly active users of their DaaS offerings on 1 April 2025
- 30,000 virtual machines under management on 1 April 2025 The user and virtual machine volumes must relate to use by organizations; consumer use does not count for inclusion
Regions: DaaS must be available in at least two regions. The regions considered in this Magic Quadrant are:
- North America
- For the scope of this research, we defined North America as the U.S., Canada and Mexico.
- Europe
- For the scope of this research, we defined Europe as the sum of Western and Eastern Europe.
- Gartner defines Western Europe as including the following countries: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and the U.K. We define Eastern Europe as including the following countries: Albania, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Croatia, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Macedonia, Moldova, Montenegro, Poland, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Türkiye, and Ukraine.
- Asia (excluding China [Region] but including the Pacific)
- For the scope of this research, we included Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, South Korea, Japan, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Philippines, Sri Lanka, Vietnam
- China [Region]
- The Chinese mainland
- Hong Kong
- Taiwan
- Latin America
- For the scope of this research, we included Brazil, Chile and Argentina
- Middle East and Africa
Support services must be available in each of the regions that the vendor operates within for coverage during daytime working hours (approximately 8:00am to 5:00pm) in at least one time zone per region.
Technical capabilities relevant to Gartner clients: Features assessed must be generally available on or before 1 April 2025:
Vendors offering DaaS can be in any or all the following configurations:
- Self-assembled DaaS: Self-assembled DaaS services are where the client selects a cloud-based virtualization broker and integrates this with a customer-defined infrastructure as a service.
- Vendor-assembled DaaS: Vendor-assembled services incorporate a cloud-based virtualization broker integrated with a cloud infrastructure. The vendor is responsible for orchestration of all infrastructure services upon which the virtual desktops operate.
- Vendor-managed DaaS: Vendor-managed DaaS services are where the vendor provides a virtualization platform, cloud infrastructure, and the management of virtual desktops. Note: While system integrators provide these offerings, their services are not covered here. They are covered by the outsourced managed workplace services Magic Quadrant.
Vendors must include the following services to qualify:
- Self-assembled DaaS services are where the client selects a cloud-based virtualization broker and integrates this with a customer-defined infrastructure as a service.
- Vendor-assembled services incorporate a cloud-based virtualization broker integrated with a cloud infrastructure. The vendor is responsible for orchestration of all infrastructure services upon which the virtual desktops operate.
- Vendor-managed DaaS services are where the vendor provides a virtualization platform, cloud infrastructure, and the management of virtual desktops. Note: While system integrators provide these offerings, their services are not covered here. They are covered by the outsourced managed workplace services Magic Quadrant.
Vendors must include the following services to qualify:
- Provide a managed control plane for the solution as part of the base license or usage fees.
- Any additional management software required to operate the virtual desktop environment.
- Maintenance, updates and upgrades to all cloud infrastructure and management software required to operate the DaaS platform.
- Unique intellectual property (IP) that is critical to DaaS operations and/or user experience. A vendor that solely integrates and orchestrates other vendors’ platforms or services would not qualify.
- A remote desktop protocol to provide secure access from an external user’s device to the DaaS virtual machines.
Provide a desktop experience that can include:
- A hosted Windows or Linux server operating system that allows multiple sessions per server delivering an individual desktop experience to each user
- A hosted Windows or Linux server operating system that allows a single session per server delivering a desktop experience to users
- A hosted Windows or Linux desktop client operating system that allows a single session per operating system virtual machine
- A hosted Windows or Linux desktop client operating system that allows multiple sessions per operating system virtual machine to deliver individual experiences to each user
- Persistent or nonpersistent VMs that are assigned to an individual or within a pool
Vendors will not qualify if they only provide these services, though these additional services may be provided:
- Hosted Windows or Linux application virtualization where the application remains on the DaaS infrastructure and is accessed via the remote desktop protocol
- Hosted macOS services
- Unified workspaces
- Local hypervisors
- Managed services Endpoint security and posture checking, which may optionally include workspace biometric assessments
- Additional value-added features from either their own portfolio of products or thirdparty products
Customer Interest Index: As more than 20 vendors qualified for this Magic Quadrant, Gartner’s Customer Interest Index was used to identify the top 20 vendors in terms of customer interest. Data inputs used to calculate DaaS customer interest include a balanced set of measures, such as:
- Gartner customer search, inquiry volume
- and trend data Volume of job listings specifying experience with the DaaS offering as a job requirement on job placement boards (e.g., LinkedIn, Indeed) and/or on a range of employment websites in the U.S., Europe, and the China region
- Frequency of mentions as a competitor to other DaaS vendors within reviews on the Gartner Peer Insights forum from March 2024 through April 2025
- Social media presence and engagements
Honorable Mentions
Gartner tracks more than 30 vendors in the DaaS space. Although this research identifies 16 vendors that have met our inclusion criteria, the exclusion of a vendor does not mean that the vendor and its products lack viability. Described below are several noteworthy vendors that did not meet all of our inclusion criteria, but could be appropriate for clients, contingent on requirements:
Google (Cameyo):
In 2024, Google acquired Cameyo, which provides virtual app delivery — the ability to virtualize Windows, Linux and internal web apps instead of delivering a full desktop, resulting in lower infrastructure and cloud hosting costs. Cameyo’s platform supports both CPU-based and GPU-accelerated applications and enables access to apps from ChromeOS, Windows, macOS, iOS, Android and HTML5 endpoints. With a focus on application delivery, it is a top choice for delivering Windows applications to ChromeOS devices, and is frequently included in large ChromeOS deployments. Cameyo supports multiple regions, with 80% of its volume in North America and EMEA, and the remaining users in Latin America and Asia/Pacific. Cameyo did not meet the inclusion criterion to provide a full virtual desktop experience
Leostream:
Leostream provides control plane and management tools that enable virtual desktops on-premises, in infrastructure-as-a-service deployments and also in public clouds, such as on AWS through an integration with Amazon WorkSpaces Core. Leostream was founded in 2002 and has traditionally focused on clients that require high levels of configuration in their VDI solutions. Its offering has matured and now addresses a broader range of privileged remote access, VDI, and DaaS use cases. Leostream did not meet the inclusion criterion for a managed control plane service.
Evaluation Criteria
Ability to Execute
Gartner analysts evaluate vendors on the viability of their DaaS offerings; their effectiveness in the market; and their growth, client retention and reputation.
Product: This criterion looks at the breadth and depth of the vendor’s DaaS offerings, whether its capabilities match what is required by enterprise clients, and its track record on delivering its roadmap.
Overall viability: This criterion includes an assessment of the organization’s overall financial health, as well as the financial and practical success of the business unit. It considers the likelihood of the organization to continue to offer and invest in the product, as well as the product’s position in the vendor’s current portfolio. Consideration is given to the sustainability of investment/ownership structure, profitability, leadership stability, organizational and partner scalability, and year-over-year product revenue growth.
Sales execution: This criterion looks at the vendor’s capabilities in all presales activities and the structure that supports them. This includes deal management, pricing and negotiation, presales support, and the overall effectiveness of the sales channel. Consideration is given to the clarity and competitiveness of the vendor’s packaging and pricing model, sustainability of new business growth, and ability to replace competitors.
Market responsiveness: This criterion looks at a vendor’s ability to respond, change direction, be flexible and achieve competitive success as opportunities develop, competitors act, customer needs evolve and market dynamics change. This criterion also considers tenure in the market, product vision, value proposition and quality of the vendor’s roadmap. Marketing execution: This criterion looks at the clarity, quality, creativity and efficacy of programs designed to deliver the vendor’s message in order to influence the market, promote the brand, increase awareness of products and establish a positive identity in the minds of customers. This mind share can be driven by a combination of publicity, promotional activity, thought leadership, social media, referrals and sales activities. Consideration is given to a vendor’s use of various channels and creation of thoughtleading content, as well as overall market awareness of the vendor’s DaaS offerings.
Customer experience: This criterion covers the products, services and/or programs that enable customers to achieve anticipated results with the products evaluated. Specifically, this includes quality buyer interactions, technical support and account support. This may also include ancillary tools, customer success programs, availability of user groups, service-level agreements and so on. Consideration is given to general customer feedback and related case studies.
Operations: This criterion looks at the ability of the vendor to meet goals and commitments. Factors include the quality of the organizational structure, skills, experiences, programs, systems and other vehicles that enable the organization to efficiently operate and effectively scale.
Criteria for product, overall viability, and sales execution/pricing are key drivers for a successful, high-scale product. These evaluation criteria are high to ensure we can highlight the vendors most viable to clients globally.
Market responsiveness and customer experience represent the maturing nature of the DaaS market, customer success and experience-focused functionality. Market responsiveness was rated high in 2024 and has decreased to medium in 2025 due to fewer significant shifts in market direction as the industry matures.
Marketing execution focuses on customer awareness. Many DaaS offerings with poor awareness remain viable offerings.
The Ability to Execute criteria used in this Magic Quadrant are listed in Table 1. For additional details on each criterion, see the Evaluation Criteria Definitions section.
Table 1: Ability to Execute Evaluation Criteria
| Evaluation Criteria | Weighting |
|---|---|
| Product or Service | High |
| Overall Viability | High |
| Sales Execution/Pricing | High |
| Market Responsiveness/Record | Medium |
| Marketing Execution | Low |
| Customer Experience | Medium |
| Operations | High |
Source: Gartner (August 2025)
Completeness of Vision
Gartner analysts evaluate vendors on their ability to understand current market opportunities and to create and articulate their vision for future market direction, innovation, customer requirements and competitive forces. Ultimately, vendors are rated on their vision for the future and on how well that maps to Gartner’s position.
Market understanding: This criterion considers a vendor’s ability to understand customer needs and translate them into products. Vendors that show a clear vision of their market listen, understand customer demands, and can shape or enhance market changes. Consideration is given to a vendor’s unique value to the market, understanding of external market forces, and alignment with customer objectives and use cases.
Marketing strategy: This criterion looks for clear, differentiated messaging consistently communicated internally and externalized through social media, advertising, customer programs and positioning statements. Consideration is given to overall ability to communicate a unique value proposition, effectively use various marketing channels and address needs of target buyer personas.
Sales strategy: This criterion considers whether the vendor has a sound strategy for selling that uses the appropriate networks, including direct and indirect sales, marketing, service, communication, and partners that extend the scope and depth of market reach, expertise, technologies and its customer base. Consideration is given to pricing and bundling, sales channels, and sales partnership strategies.
Product strategy: This criterion evaluates whether a vendor’s approach to product development and delivery emphasizes market differentiation, functionality, methodology and features that cover current and future requirements. Consideration is given to the vendor’s vision to deliver expanded capabilities and a consistent product release cadence, as well as its ability to ensure that its roadmap addresses common customer needs and use cases.
Business model: This criterion looks at the design, logic and execution of the vendor’s business proposition to achieve continued success. Consideration is given to the vendor’s business, value proposition and unique capabilities (for example, patents, people, technology and data).
Vertical industry strategy: This criterion considers a vendor’s strategy to direct resources, skills and products to meet the specific needs of individual market segments, including verticals. Additional consideration is given to the most common industries among customers, specific target industries and compliance with common industry regulations or certifications.
Innovation: This criterion looks at direct, related, complementary and synergistic layouts of resources, expertise or capital for investment, consolidation, defensive or preemptive purposes. Consideration is given to the strength of the DaaS offering roadmap.
Geographic strategy: This criterion looks at the provider’s strategy to direct resources, skills and offerings to meet the specific needs of geographies outside its “home” or native geography — either directly or through partners, channels and subsidiaries — as appropriate for that geography and market. Additional consideration is given to the number of employees allocated to different regions, tailoring of go-to-market or product strategy to address regional differences, and the depth and scope of partners available in countries with existing and new customers.
Criteria for market understanding, sales strategy, offering (product) strategy, business model, innovation, and geographic strategy have the most influence on whether a client will purchase the DaaS offering and its future health. The criteria weighting for geographic strategy increased from medium in 2024 to high in 2025 because several new vendors are qualifying that have distinct market focus and penetration in China and Asia, compared with established vendors with coverage for the largest spending regions of North America and Europe.
Criteria for vertical/industry strategy highlight DaaS is adopted by a broad set of verticals.
Criteria for marketing strategy emphasize how vendors plan to build awareness of their offering and increase mind share among prospects and clients.
The Completeness of Vision criteria used in this Magic Quadrant are listed in Table 2. For additional details on each criterion, see the Evaluation Criteria Definitions section.
Table 2: Completeness of Vision Evaluation Criteria
| Evaluation Criteria | Weighting |
|---|---|
| Market Understanding | High |
| Marketing Strategy | Low |
| Sales Strategy | High |
| Offering (Product) Strategy | High |
| Business Model | High |
| Vertical /Industry Strategy | Medium |
| Innovation | High |
| Geographic Strategy | High |
Source: Gartner (August 2025)
Quadrant Descriptions
Leaders
Leaders exhibit strong execution and vision scores and have proven their success in the market by gaining market share. Leaders have successfully shown they can attract clients new to desktop virtualization, as well as those migrating from on-premises VDI solutions. They address a broad range of use cases and have scale across multiple regions. They bring innovation to their offerings and have significant investment in their DaaS capabilities.
Challengers
Challengers exhibit a strong set of technologies, marketing and sales execution, and intellectual property, as also exhibited by Leaders, but they tailor solutions to specific market segments, regions or use cases. They may be satisfied with serving their current customer base or market, or they may lack the strategic support, direction or desire to compete in the Leaders quadrant.
Visionaries
Visionaries exhibit strong capabilities in their current offerings and a complete set of functionalities to address common use cases. However, the vendor’s size, size of its installed base, platform breadth or integration points make it appropriate for some, but not all, buyers. Characteristics of visionaries in this Magic Quadrant include a broad range of DaaS capabilities that have the opportunity to scale, are applicable to all industry verticals and have broad global reach.
Niche Players
Niche Players exhibit leadership in specific use cases, market segments or verticals. However, their offerings fail to provide a breadth of features that make them relevant to all buyers, regardless of vertical, geographic market or use case. Characteristics observed in Niche Players for this Magic Quadrant include high-performance workloads, rich graphics enabled by GPUs, focus on specific regions, and focus on specific industry verticals and capabilities that, while available for sale as DaaS offerings, are commonly deployed by others to enable white-label DaaS offerings.
Context
The goal of any Magic Quadrant is to provide a level view of comparable products (size, capability and corporate structure) to address the demands of a wide variety of buyers. Not every organization’s requirements are identical. We encourage clients to review the accompanying Critical Capabilities for Desktop as a Service to evaluate use cases and functional requirements. Use this research to align industry expertise, vision, technology and cost requirements to the right vendor, regardless of the vendor’s quadrant.
Acronym Key and Glossary Terms
Gartner Customer Interest Indicator (CII)
The Customer Interest Indicator assesses client inquiry volumes, Gartner Peer Insights mentions, social media followers, Gartner search, Google Trends and web traffic analysis.
Evidence
1 Forecast: Public Cloud Services, Worldwide, 2023-2029, 2Q25 Update
Evaluation Criteria Definitions
Ability to Execute
Product/Service: Core goods and services offered by the vendor for the defined market. This includes current product/service capabilities, quality, feature sets, skills and so on, whether offered natively or through OEM agreements/partnerships as defined in the market definition and detailed in the subcriteria.
Overall Viability: Viability includes an assessment of the overall organization's financial health, the financial and practical success of the business unit, and the likelihood that the individual business unit will continue investing in the product, will continue offering the product and will advance the state of the art within the organization's portfolio of products.
Sales Execution/Pricing: The vendor's capabilities in all presales activities and the structure that supports them. This includes deal management, pricing and negotiation, presales support, and the overall effectiveness of the sales channel.
Market Responsiveness/Record: Ability to respond, change direction, be flexible and achieve competitive success as opportunities develop, competitors act, customer needs evolve and market dynamics change. This criterion also considers the vendor's history of responsiveness.
Marketing Execution: The clarity, quality, creativity and efficacy of programs designed to deliver the organization's message to influence the market, promote the brand and business, increase awareness of the products, and establish a positive identification with the product/brand and organization in the minds of buyers. This "mind share" can be driven by a combination of publicity, promotional initiatives, thought leadership, word of mouth and sales activities.
Customer Experience: Relationships, products and services/programs that enable clients to be successful with the products evaluated. Specifically, this includes the ways customers receive technical support or account support. This can also include ancillary tools, customer support programs (and the quality thereof), availability of user groups, service-level agreements and so on.
Operations: The ability of the organization to meet its goals and commitments. Factors include the quality of the organizational structure, including skills, experiences, programs, systems and other vehicles that enable the organization to operate effectively and efficiently on an ongoing basis.
Completeness of Vision
Market Understanding: Ability of the vendor to understand buyers' wants and needs and to translate those into products and services. Vendors that show the highest degree of vision listen to and understand buyers' wants and needs, and can shape or enhance those with their added vision.
Marketing Strategy: A clear, differentiated set of messages consistently communicated throughout the organization and externalized through the website, advertising, customer programs and positioning statements.
Sales Strategy: The strategy for selling products that uses the appropriate network of direct and indirect sales, marketing, service, and communication affiliates that extend the scope and depth of market reach, skills, expertise, technologies, services and the customer base.
Offering (Product) Strategy: The vendor's approach to product development and delivery that emphasizes differentiation, functionality, methodology and feature sets as they map to current and future requirements.
Business Model: The soundness and logic of the vendor's underlying business proposition.
Vertical/Industry Strategy: The vendor's strategy to direct resources, skills and offerings to meet the specific needs of individual market segments, including vertical markets.
Innovation: Direct, related, complementary and synergistic layouts of resources, expertise or capital for investment, consolidation, defensive or pre-emptive purposes.
Geographic Strategy: The vendor's strategy to direct resources, skills and offerings to meet the specific needs of geographies outside the "home" or native geography, either directly or through partners, channels and subsidiaries as appropriate for that geography and market.
Industry-recognized and certified to support your IT needs
Trusted by 1,700+ mid-size and enterprise companies, we operate as an extension of your team—solving problems with urgency and accountability so you can focus on strategy, not firefighting. We are not just another MSP. We're your force multiplier that bring proven frameworks and real-world experience to help you secure, scale and streamline operations with fewer resources. Stop juggling vendors. Stop fighting uphill battles. Work with an IT partner who gets IT.






















